Fluid Dynamic Simulation Using Lattice Boltzmann Model
Numerical Simulation of Fluid Flow Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method: A Study on Convergence and Stability
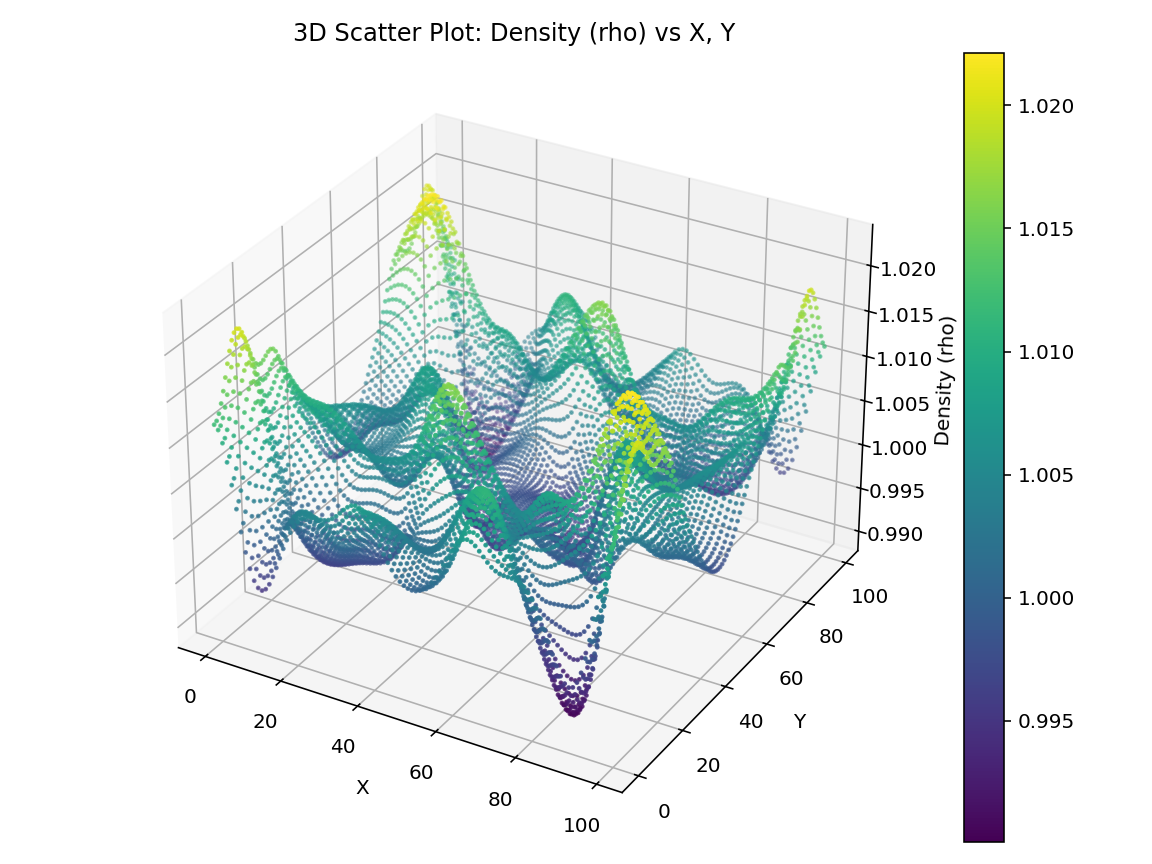
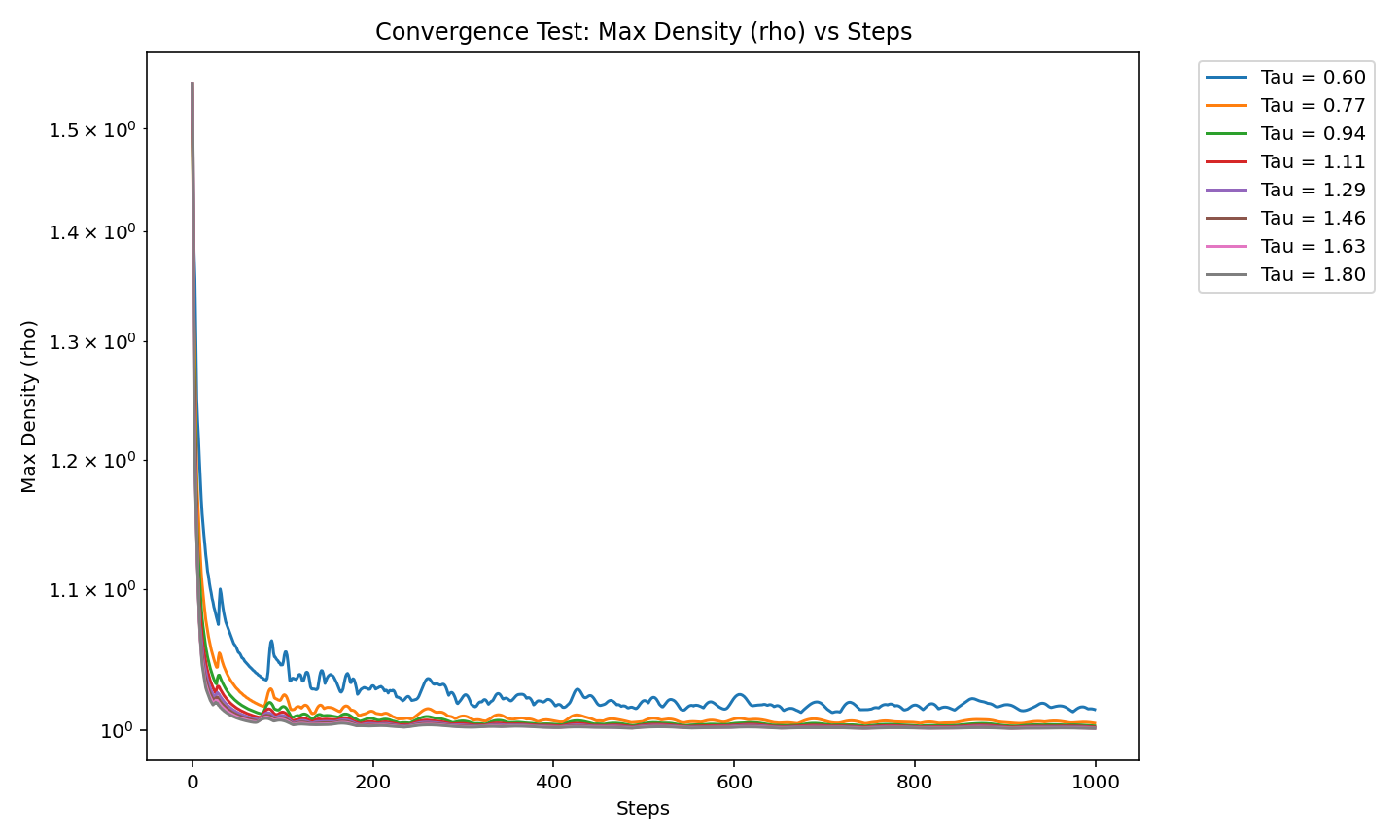
The Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) is a versatile and efficient numerical approach for solving fluid dynamics problems, particularly the Navier-Stokes equations. This project explores the application of LBM to a two-dimensional (2D) fluid simulation, focusing on the convergence and stability of solutions for varying relaxation times (τ). The simulation captures fluid dynamics with embedded density peaks and velocity distributions using the D2Q9 model, enhanced with non-linear equilibrium corrections. To assess stability, a convergence test was conducted across multiple τ values, revealing critical thresholds for numerical instability. The results provide insight into the delicate balance between computational accuracy and physical fidelity. This project includes visualizations such as time-evolving density maps, 3D scatter plots, and convergence behavior in logarithmic scale, making it accessible to a broad audience.
Here’s the entire code on Github
If you want to read the full report illustrating the theory, approach taken, and results then please click here.
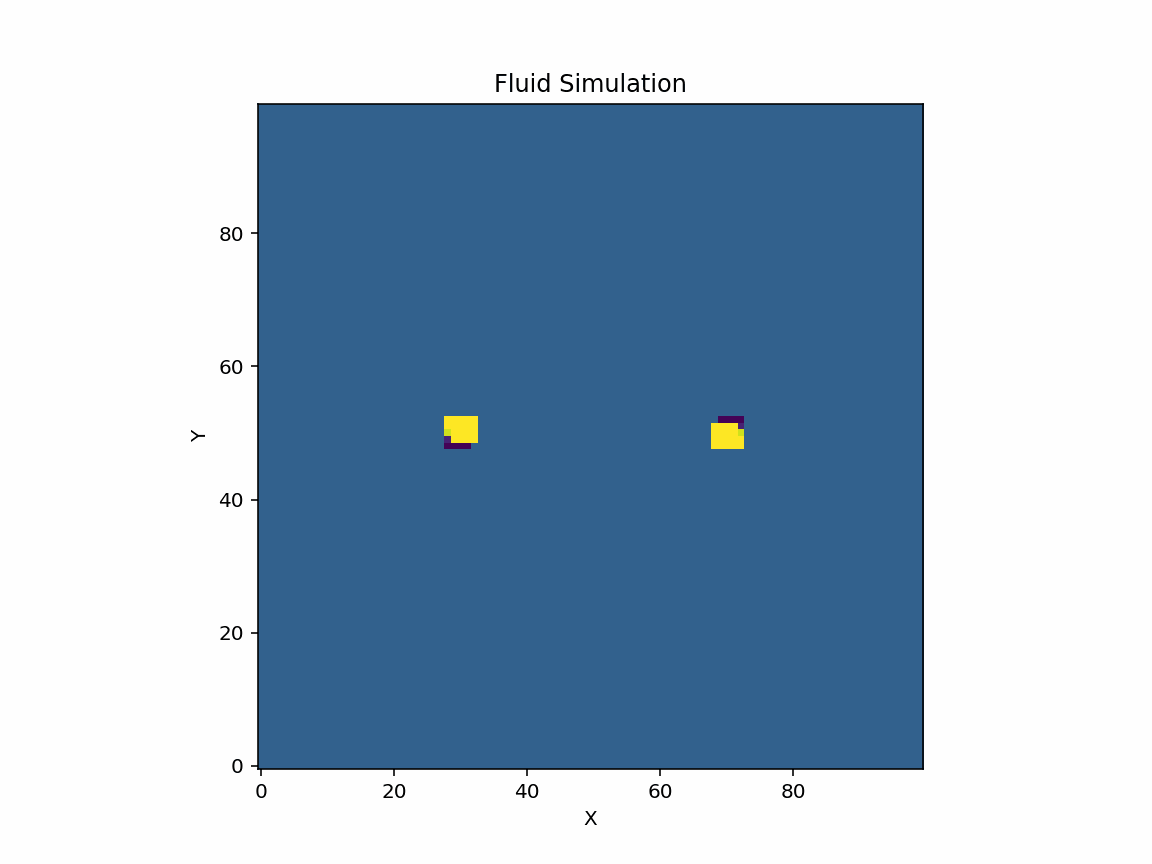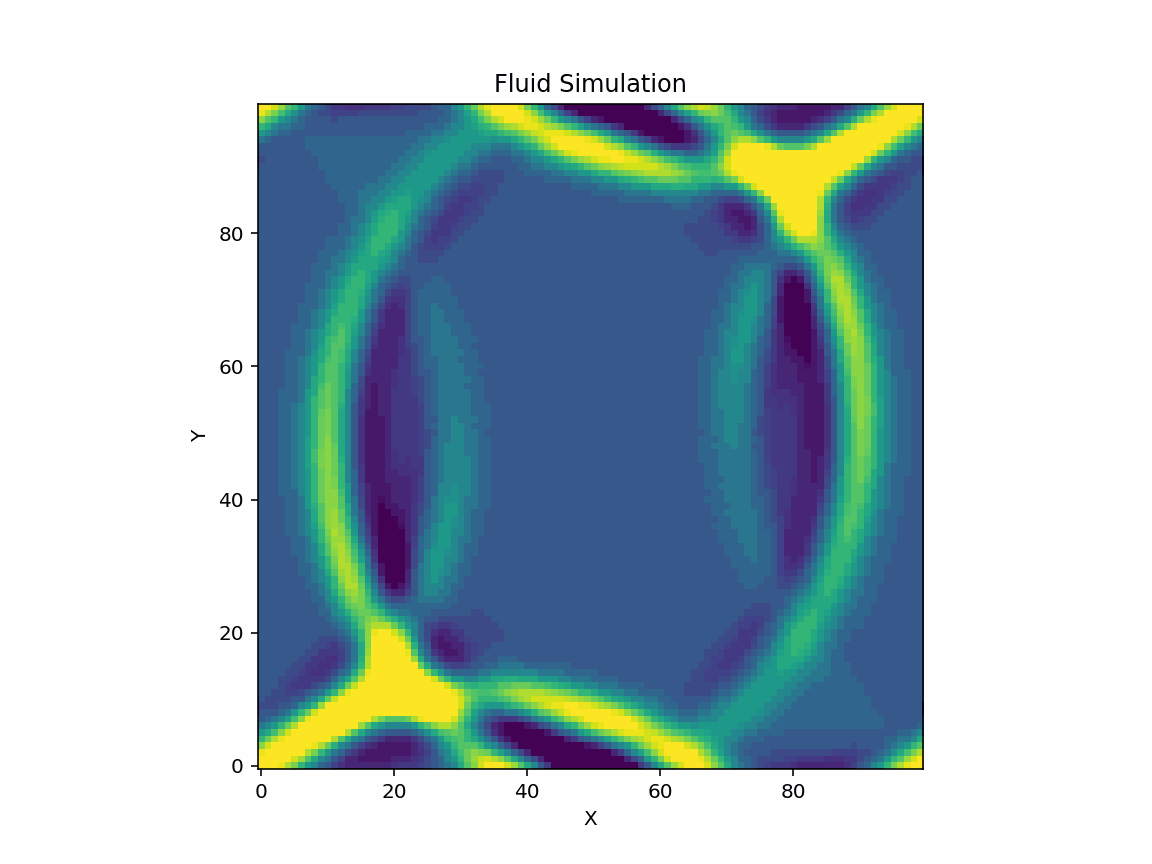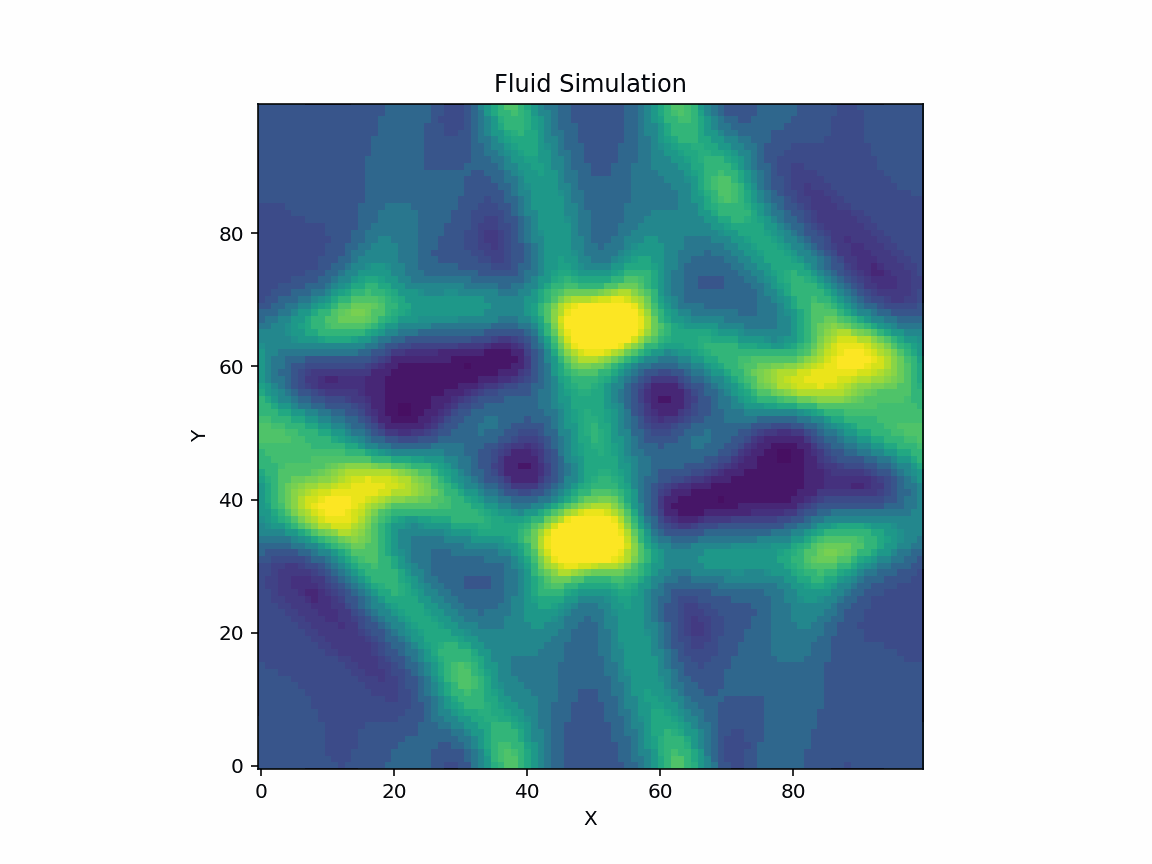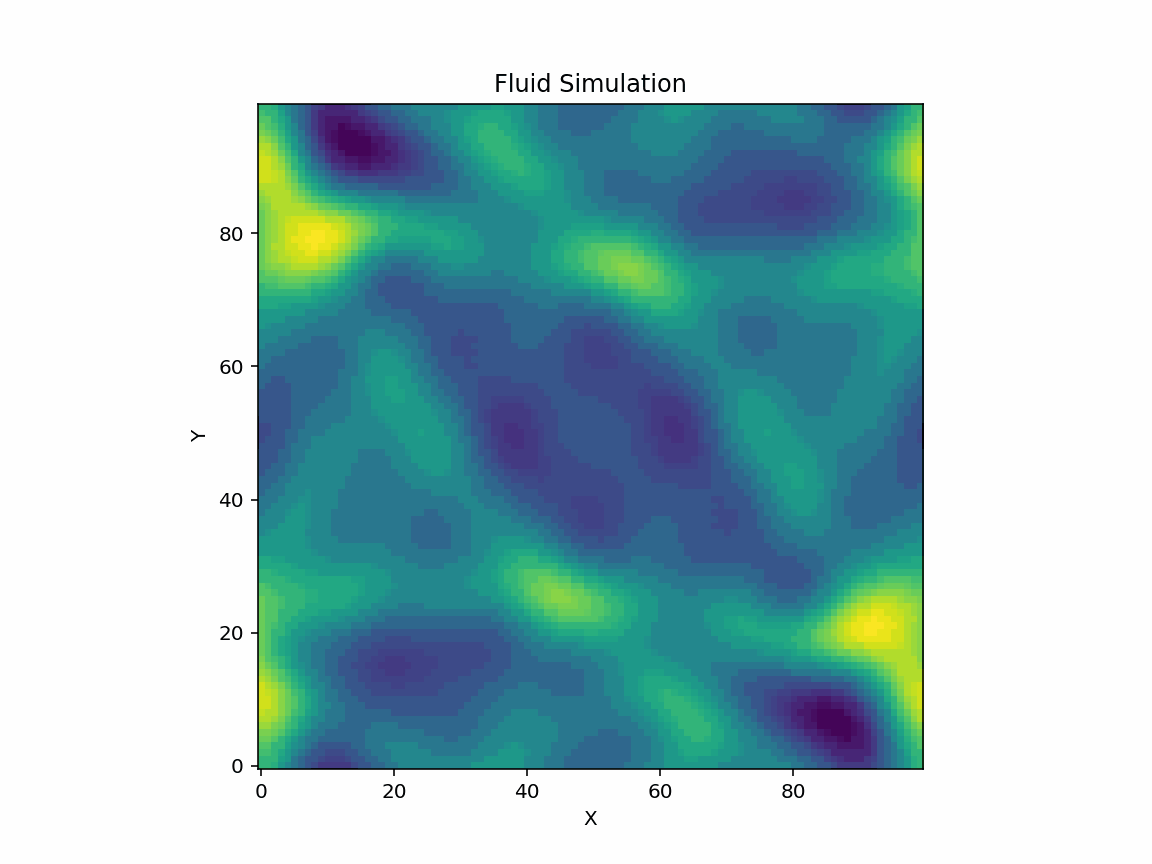
Here are the some visualisations from the project.